Attrities is a term that spans multiple fields, from healthcare to business. In medicine, it refers to joint inflammation and pain that impacts mobility and quality of life. In business, attrities describe gradual losses such as employee turnover, customer drop-off, or declining revenue. Understanding attrities—whether in the body or in an organization—is essential for prevention and management. This guide explores types, causes, treatments, and strategies to prevent attrities, helping you maintain healthy joints and robust business systems.
Discover attrities in health and business: causes, types, treatments, and strategies to prevent joint pain and organizational decline for long-term success…
What Are Attrities?
Attrities is a versatile concept applied in both healthcare and business. In medical terms, it refers to the gradual degradation of joint function accompanied by inflammation, often resembling arthritis. In a business context, attrities refers to the gradual decline of critical organizational resources, such as employees, customers, revenue, or performance.
Recognizing attrities is essential in both scenarios. In health, early detection prevents irreversible joint damage. In business, monitoring attrities helps organizations detect weaknesses, reduce losses, and maintain stability. Ignoring attrities in either field can lead to severe long-term consequences.
Attrities in Health: Joint Pain Explained
Joint health is central to human mobility. Attrities in health represent a spectrum of conditions where inflammation and wear lead to discomfort, stiffness, and loss of flexibility. The condition affects millions globally and can impact daily life, from climbing stairs to holding a pen.
Types of Joint Attrities
- Osteoarthritis (Degenerative Attrities)
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of attrities, often described as “wear and tear” arthritis. Over time, cartilage—the protective cushion between bones—breaks down. Without this buffer, bones rub together, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. Commonly affected areas include knees, hips, hands, and the spine. - Rheumatoid Arthritis (Inflammatory Attrities)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks its own joint tissue. Unlike osteoarthritis, RA affects the same joints on both sides of the body. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, fatigue, and sometimes low-grade fever or appetite loss.
- Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis occurs in individuals with psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. Joint pain, swelling, and stiffness accompany skin symptoms. This type of attrities can affect fingers, toes, and the spine, sometimes leading to severe mobility issues if untreated. - Gout (Metabolic Attrities)
Gout is caused by uric acid crystal accumulation in joints, leading to sudden, intense pain. The big toe is the most commonly affected area, but knees, ankles, and elbows may also experience flares. Untreated gout can cause chronic joint damage and kidney complications.
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of attrities is crucial for early intervention:
- Persistent Joint Pain: Can range from dull aches to sharp, stabbing sensations. Pain typically worsens with movement and flare-ups.
- Swelling & Redness: Inflamed joints may appear puffy, red, or warm to touch.
- Stiffness: Especially noticeable in the morning or after prolonged inactivity.
- Reduced Mobility: Difficulty bending, straightening, or moving joints fully.
- Crepitus: Grinding, popping, or cracking sounds caused by cartilage wear.
Early detection of these symptoms allows for effective management and slows progression, improving long-term quality of life.
Causes of Joint Attrities
Attrities develop from multiple factors:
- Aging: Cartilage naturally deteriorates over time, making joints more susceptible to damage.
- Genetics: Family history can increase vulnerability to arthritis and related disorders.
- Previous Injuries: Old fractures, ligament tears, or joint trauma accelerate wear and tear.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like RA cause the body to attack its own joints.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, inactivity, and poor diet increase stress on joints and exacerbate inflammation.
Medical Treatments for Joint Attrities
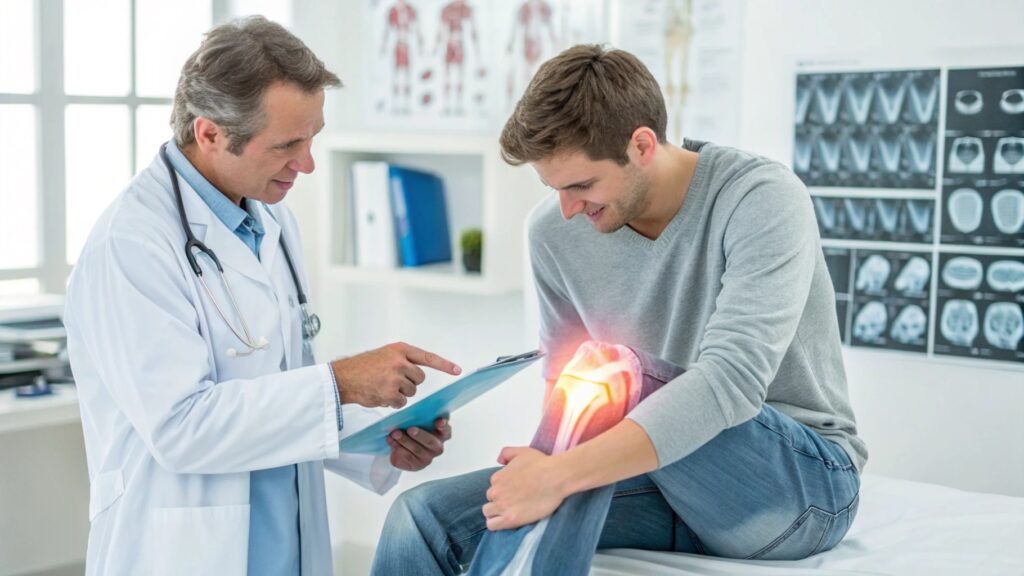
Medications
Medications can help reduce pain and inflammation:
- Analgesics: Over-the-counter pain relievers for mild discomfort.
- NSAIDs: Reduce inflammation and pain (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen).
- Corticosteroids: Targeted injections for severe inflammation, offering temporary relief.
- DMARDs & Biologics: Slow progression in autoimmune types like RA.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy strengthens muscles supporting joints, improves mobility, and reduces pain. Common activities include swimming, cycling, resistance training, yoga, and gentle stretching.
Therapists design programs tailored to individual needs, balancing flexibility, strength, and joint protection. Regular exercise also supports mental health and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, nuts, leafy greens, and berries help reduce joint inflammation.
- Weight Management: Losing even a few pounds decreases pressure on weight-bearing joints.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Warm showers or heating pads relax muscles; ice packs reduce swelling.
- Stress Management & Sleep: Meditation, deep breathing, and quality sleep improve recovery and reduce pain.
Business Attrities: Understanding Organizational Decline

Attrities in business refers to gradual losses in employees, customers, revenue, or operational performance. These losses can accumulate silently, affecting long-term growth and stability.
Understanding business attrities allows organizations to implement corrective measures and prevent decline before it becomes critical.
Types of Business Attrities
- Employee Attrities: Resignations, retirements, or burnout. High rates indicate deeper organizational issues like poor culture, lack of growth opportunities, or weak leadership.
- Customer Attrities: Customers who stop buying or switch to competitors. Causes include poor service, lack of engagement, or declining product quality.
- Revenue Attrities: Gradual loss of profits due to market shifts, rising costs, or reduced customer retention.
- Digital Attrities: Decline in app usage, website traffic, or social media engagement.
- Operational Attrities: Equipment failure, process inefficiencies, or declining productivity.
Causes of Attrities in Organizations
- Poor leadership and communication
- Lack of innovation or outdated technology
- Weak employee or customer retention strategies
- Economic challenges or market competition
Strategies to Reduce Attrities
- Improve Employee Experience: Offer growth opportunities, recognition, and supportive environments.
- Strengthen Customer Loyalty: Personalize experiences, enhance service quality, and maintain consistent engagement.
- Upgrade Technology: Automate processes, modernize platforms, and simplify digital experiences.
- Enhance Data Analysis: Track trends, predict potential losses, and take proactive measures.
- Invest in Innovation: Regularly updating products and processes reduces attrition risks.
Organizations that actively monitor and manage attrities maintain stronger teams, happier customers, and sustainable profits.
Preventing Attrities: Health and Business

Health Prevention Tips:
- Engage in regular low-impact exercise
- Maintain a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet
- Protect joints during physical activity
- Seek early medical advice for pain or stiffness
Business Prevention Tips:
- Monitor employee and customer metrics
- Foster a positive company culture
- Implement retention strategies
Use analytics to predict trends and prevent losses
FAQs About Attrities
1. Can joint attrities be cured completely?
Most forms are chronic, but symptoms can be managed with medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
2. Is exercise safe for joint attrities?
Yes, low-impact activities like swimming, yoga, and cycling strengthen joints without causing further damage.
3. How can businesses reduce attrities?
By improving employee satisfaction, customer engagement, and operational efficiency.
4. Does diet affect joint attrities?
Yes, anti-inflammatory foods and proper nutrition help reduce joint inflammation.
5. At what age does attrities typically start?
Joint attrities often appear after 40–50, but injuries, autoimmune issues, or lifestyle factors can cause earlier onset.
Conclusion
Attrities affects both human health and organizational performance. In joints, it leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, while in businesses, it manifests as gradual declines in employees, customers, or revenue. Recognizing early signs, taking preventive measures, and implementing effective management strategies can slow or reverse its impact. By combining medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and proactive business practices, you can maintain healthy joints, strong teams, and sustainable growth for long-term success.

